AR in Education Apps – Transforming the Future of Learning
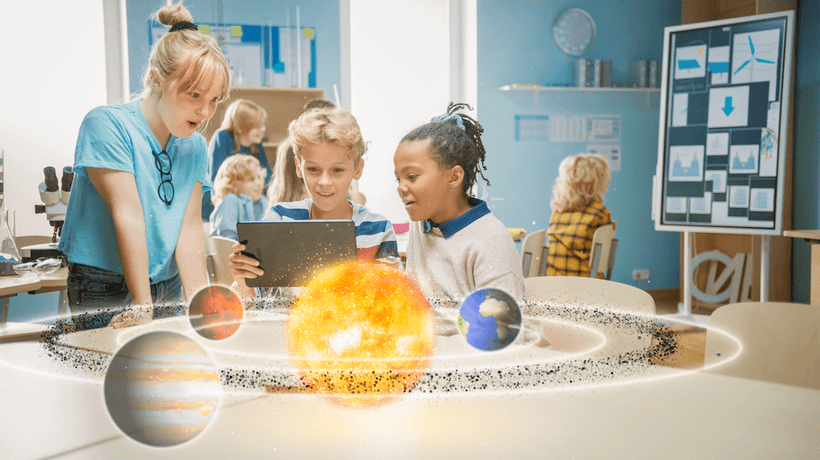

Discover how AR in education apps is changing classrooms with interactive, 3D, and immersive learning. Learn benefits, challenges, and future trends.
Augmented Reality (AR) in education apps is rapidly changing how students learn, teachers teach, and educational institutions deliver content. By overlaying digital content (3D models, animations, interactive elements) on the real world, AR creates immersive, context-rich experiences that deepen understanding and engagement.
In this article, we will explore:
- What AR in education apps means
- Benefits and impact
- Use cases and examples
- Technical and pedagogical challenges
- Design and development best practices
- SEO and marketing considerations
- Future trends
Let’s dive in.
What Does “AR in Education Apps” Mean?

Definition and Core Components
When we say AR in education apps, we refer to mobile or web-based applications that leverage augmented reality technology to overlay virtual content over real-world surroundings, providing learners with an enriched, interactive learning experience.
Key components include:
- Device sensors & camera: Used to track the real-world environment
- Rendering engine / AR SDKs: Tools like ARCore, ARKit, Vuforia, Unity AR Foundation, etc.
- Marker-based / markerless tracking: Some AR uses visual markers to align virtual objects; others use spatial awareness without markers
- Interactive content: 3D models, animations, quizzes, audio, video
- Feedback / interaction loop: Users can touch, rotate, zoom, trigger animations
How AR in Education Apps Works (Simplified)
Here’s a simple flow of how an AR educational app functions:
- The app accesses the device camera and sensors.
- It recognizes a marker or environment (plane, surface, image).
- Virtual content is overlaid onto that real-world reference.
- Learner interacts with it (rotates, explores, triggers animations).
- App gives feedback or next steps.
In many AR education apps, the content is contextually tied to a textbook, poster, or the real environment (e.g. pointing phone to a human body diagram brings up organs in 3D).
AR educational apps allow students to “see inside” abstract or microscopic concepts—for example, the human heart pumping blood, molecular structures, or mechanical parts of a machine.
Why AR in Education Apps Matters: Benefits & Impact
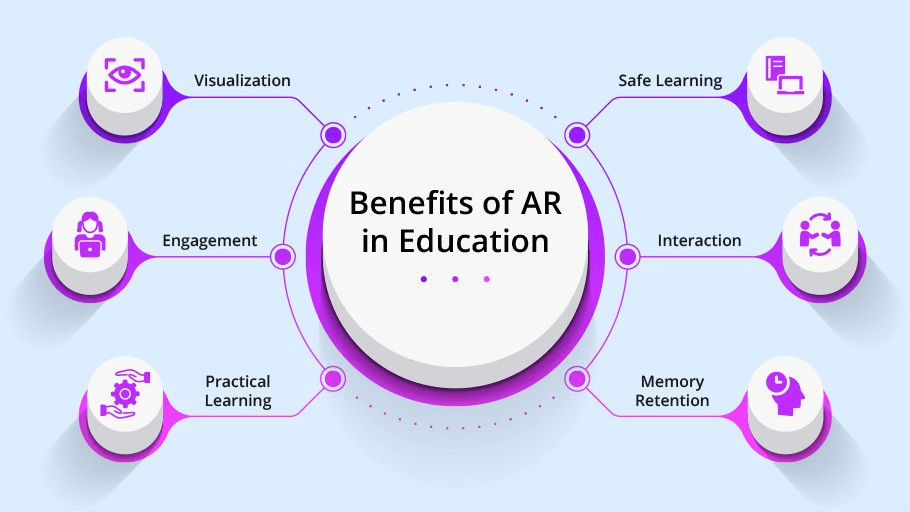
Integrating AR in education apps offers many potential advantages. Let’s look at evidence and real-world impacts.
Enhanced Engagement & Motivation
- AR introduces a “wow factor” — students are curious and excited to use it.
- It transforms passive reading or lectures into interactive, exploratory experiences.
- Studies show that AR can increase student motivation and time-on-task. (E.g. students found AR lessons fun, memorable) ERIC+1
Improved Understanding & Retention
- Visualizing complex or abstract concepts is easier when overlaid in 3D.
- Because learners can manipulate objects, they engage in active learning rather than just consumption.
- Research indicates that AR promotes enhanced learning achievement in many domains. ScienceDirect
- For example, marker-based AR used in physics or anatomy helps students internalize spatial relationships. ERIC
Real-World Contextual Learning
- AR bridges virtual and real worlds, adding context.
- Learners can see how abstract ideas map to actual objects in their environment.
- For example, pointing a phone at a plant could overlay roots, internal anatomy, or photosynthesis animations.
Personalized & Self-Paced Learning
- Many AR apps support self-paced navigation, letting learners explore topics at their own speed.
- The app can adapt (e.g. unlocking more complex models) as learners progress.
Safe Simulation of Experiments & Scenarios
- Some experiments or scenarios are dangerous, expensive, or impractical in classrooms (e.g. chemical reactions, surgical anatomy).
- AR in education apps can simulate these safely.
- In STEM education, virtual labs and interactive simulations are key use cases. Pixelcrayons
Increased Collaboration & Social Learning
- AR experiences can be collaborative — multiple students may view or manipulate the same virtual object from different angles.
- Teachers can guide students in augmented explorations.
Analytics & Feedback for Teachers
- AR apps can log student interactions: which parts they examined, how long, which errors they made.
- Teachers get visibility into student progress and can provide targeted support.
Real-World Use Cases of AR in Education Apps
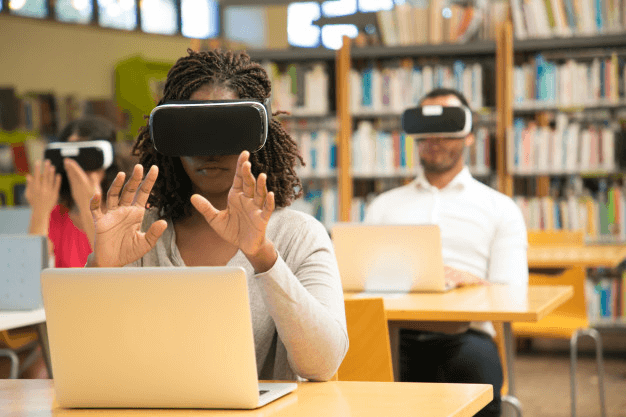

Let’s look at concrete examples and scenarios where AR in education apps is used today.
Anatomy & Medical Training
Imagine pointing your phone at a blank human silhouette and seeing internal organs, bones, muscles, and their motions in 3D. AR apps help medical students and biology learners visualize human anatomy in a more intuitive way.
For example, Arloopa was used in a university to overlay lungs into a classroom for discussions; students reported it made lessons more fun and improved creativity. ERIC
Physics, Chemistry & STEM Visualizations
- AR can show molecular structures, atomic orbits, chemical bonding in 3D.
- Physics phenomena like magnetic fields, forces, or circuits can be visualized and manipulated.
Interactive Textbooks & Learning Objects
- Printed textbooks or worksheets can act as markers. When scanned via AR apps, the page “comes alive” with animations or extra content (videos, quizzes).
- This transforms static content into interactive learning experiences.
Field Trips & Virtual Labs
- AR can turn real-world locations into learning zones. For example, in a botanical garden, pointing a device at a plant could bring up species info, growth history, etc.
- Lab simulations happen in AR, allowing students to experiment hands-on virtually.
Language Learning & Vocabulary (Contextual AR)
A project called VocabulARy used AR to label real-world objects with English and another language words, adding audio and keyword visualizations. This improved vocabulary learning compared to non-AR methods. arXiv
Reading & Storybooks in AR
Recent research introduced Metabook, a system that generates interactive augmented reality storybooks, combining visuals, text, AI, and avatars. The study found it increased children’s interest and deepened vocabulary retention. arXiv
Challenges & Limitations of AR in Education Apps
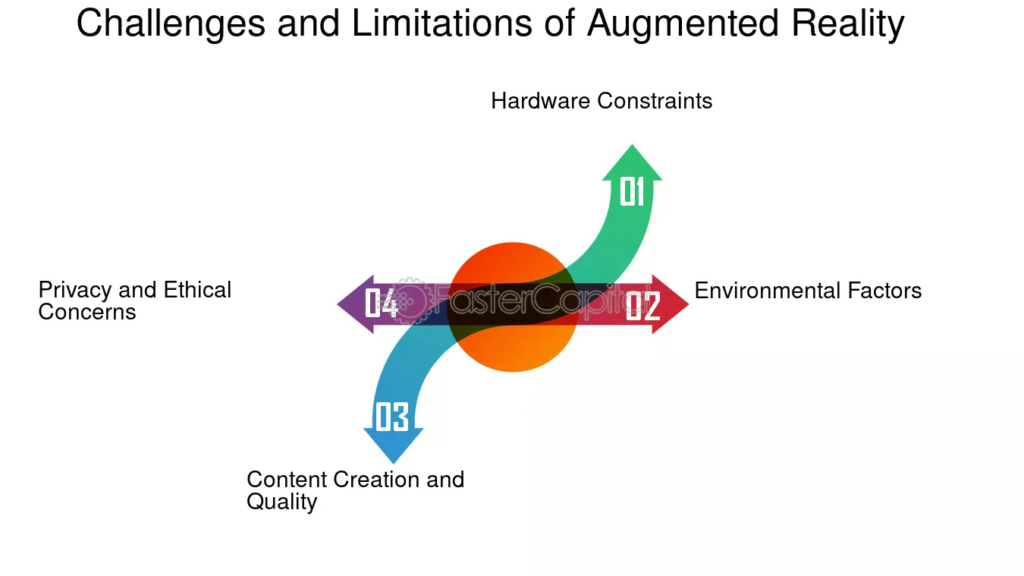
While AR in education apps offers many benefits, it also comes with challenges. Awareness of these helps in planning realistic and sustainable projects.
Technical & Hardware Constraints
- Not all students have AR-capable devices (older phones, tablets).
- AR performance depends on device sensors, computing power, battery life.
- Tracking errors, unstable overlays, or drift can degrade user experience.
Usability & User Experience Issues
- Poor UI/UX design can confuse learners or distract them.
- Excessively complex controls or navigation reduce adoption.
- Some learners may feel motion sickness or fatigue in AR.
Content Development Costs & Scalability
- Creating high-quality 3D models, animations, interactions is resource-intensive.
- Maintaining, updating AR content across curricula is challenging.
- Educational content must align with pedagogy and standards—not just flashy visuals.
Teacher Training & Adoption
- Teachers may lack familiarity with AR tools and pedagogy.
- Resistance to change or fear of technical issues can hinder uptake.
- Professional development and support are needed.
Distraction Risk & Overuse
- There’s a risk that AR becomes a novelty and distracts from learning objectives.
- Students may focus on exploring animations rather than the core concept.
Equity and Access
- Students in low-resource environments may not have compatible devices.
- Digital divide issues must be addressed to avoid widening inequality.
Integration with Curriculum & Assessment
- Aligning AR experiences to learning goals, assessment standards, and curriculum requires careful instructional design.
- Ensuring that AR does not become an “add-on” but woven into pedagogy is key.
Best Practices for Designing AR in Education Apps
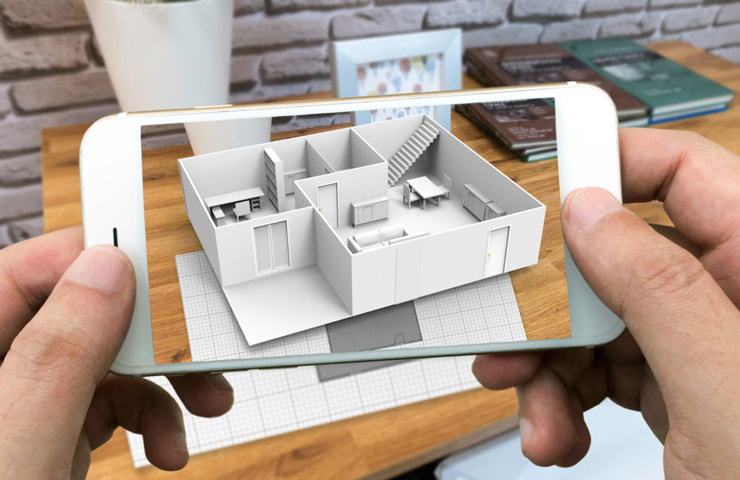

To maximize the effectiveness of AR in education apps, follow these design and implementation best practices.
Start with Learning Objectives, Not Technology
- Begin with your learning goals: which concepts are hard to teach traditionally?
- Use AR only when it adds value (e.g. making invisible objects visible, enhancing spatial reasoning).
- Avoid forcing AR everywhere—it should support pedagogy, not overshadow it.
Keep Interactions Simple & Intuitive
- Use familiar touch gestures, menus, or tutorials.
- Avoid overly complex controls or too many steps before arriving at content.
- Always include fallback or help modes.
Scaffold the Experience
- Begin with simpler interactions and gradually introduce complexity.
- Provide guided exploration or hints to avoid users getting lost.
Use Mixed Modalities (Visual + Audio + Text)
- Combine visuals with narration, captions, labels to reinforce learning.
- Use animations to show processes (e.g., flow, cause-effect).
Provide Feedback & Assessment
- After interaction, offer quizzes, prompts, or reflection questions in AR or outside it.
- Track interactions and provide analytics to both students and teachers.
Optimize Performance & Responsiveness
- Use lightweight 3D models, efficient rendering, and caching to reduce lag.
- Ensure robust tracking under varied lighting and environments.
- Test on lower-end devices to ensure broad usability.
Offline Capability & Accessibility
- Where possible, support offline use (preload assets).
- Provide alternative non-AR delivery (e.g. 2D fallback) for accessibility.
- Ensure AR apps are usable for learners with disabilities.
Teacher Tools & Content Authoring
- Enable teachers to import or build AR content easily (via authoring tools, drag-and-drop).
- Provide templates or modular content to scale across subjects.
Pilot & Iterate
- Start with pilot projects in a classroom, collect feedback, refine.
- Use iterative design to improve UX, content alignment, and stability.
Privacy, Ethics & Safety Considerations
- Avoid capturing or storing sensitive student data without consent.
- Ensure safe physical usage (students should not walk blindly while using AR).
- Use persuasive or gamified design responsibly (avoid undue pressure).
How to Develop & Deploy AR in Education Apps

Here is a roadmap and tech-stack guidance for building AR education apps.
Technology Stack & AR SDKs
Common AR tools include:
- ARCore (Android)
- ARKit (iOS)
- Unity + AR Foundation (cross-platform)
- Vuforia (marker-based + model tracking)
- WebAR (browser-based AR) Wikipedia
Many AR education apps use Unity + Vuforia or Unity + AR Foundation. In a survey of recent literature, Unity and Vuforia were predominant platforms in AR education applications. ResearchGate
Content Production Pipeline
- 3D modeling (Blender, Maya, etc.)
- Animation (rigging, keyframe, simulation)
- Asset optimization (polygon count, textures)
- Sound, narration, UI overlays
- Authoring or CMS system for content updates
Application Architecture
- Client-side AR engine + rendering
- Content management system (CMS) or backend
- Analytics and logging
- User profiles, progress tracking
- Offline caching
Deployment & Distribution
- Mobile App Stores (Google Play, Apple App Store)
- WebAR distribution (direct via browser)
- Integration into existing LMS (Learning Management Systems)
- Classroom deployment (preloaded on school devices)
Testing & QA
- Device compatibility testing across a range of phones/tablets
- Environmental testing (lighting, surfaces)
- Edge-case handling (tracking failures, interruptions)
- Usability testing with actual students and teachers
Maintenance & Updates
- Content versioning and updates
- Bug fixes, performance optimizations
- Content expansion (new modules)
- Analytics-based iteration
SEO & Marketing for AR in Education Apps

If you are building an AR education app and want it to reach your target audience, SEO and content marketing become crucial. Here’s how to align AR in education apps with SEO best practices.
Keyword Strategy & Content Planning
- Use “AR in education apps” as your main keyword, appearing in title, headers, meta descriptions.
- Supplement with long-tail variants: “augmented reality education app advantages”, “AR learning tools for schools”, “AR STEM app for education”, etc.
- Create content around use cases, tutorials, case studies, success stories.
On-Page SEO Best Practices
- Use your focus keyword in H1, at least one H2, and sprinkle in H3, H4 naturally.
- Include meta title and meta description with the keyword.
- Use alt text and captions for images (e.g. “AR app showing human anatomy”).
- Internal linking: link from related pages (e.g. blog, product pages).
- Use schema markup (e.g. EducationalApplication, SoftwareApplication) to help search engines.
Content Marketing & Thought Leadership
- Publish blog posts, case studies, whitepapers on AR in education apps.
- Share pilot deployments, results, user testimonials.
- Guest post on educational technology blogs.
- Use video demos and tutorials to drive engagement.
App Store Optimization (ASO)
- Use keyword “AR education app” in app title and subtitle (if platform allows).
- Write a compelling app description with target terms and use cases.
- Use promotional screenshots showing AR interactions.
- Encourage user ratings and reviews.
Backlink & PR Strategy
- Reach out to edtech blogs, education institutions, tech press to review your app or pilot.
- Publish research or evaluation results to academic forums.
- Offer free trials to schools or districts to generate case studies.
Local SEO (for physical school deployments)
- If you deploy in a local region or district, create landing pages optimized for your location (e.g. “AR education apps in Delhi”).
- Use Google My Business, local directories.
- Use location-based keywords in content and metadata.
Measuring Success & Key Metrics

To evaluate whether your AR education app is effective, track both learning metrics and product metrics.
Learning Outcomes & Engagement
- Pre- and post-tests to measure knowledge gains
- Time spent interacting with AR modules
- Completion rates (how many finish modules)
- Mistakes, retries, hint usage
- Surveys/interviews: learner satisfaction, perceived usefulness
Retention & Usage Metrics
- User retention (how many come back)
- Session durations
- Module drop-off points
- Frequency of usage
Conversion & Adoption Metrics
- Number of schools, classes, or students adopting
- Paid vs free usage
- Upgrade/monetization conversion rates
Technical Performance Metrics
- App crashes or failures during AR sessions
- Frame rates / latency
- Tracking/overlay accuracy issues
Feedback & Improvement Loops
- Regular feedback from teachers and students
- Usage logs to identify bottlenecks
- A/B testing of interaction designs or content
Future Trends & Outlook for AR in Education Apps
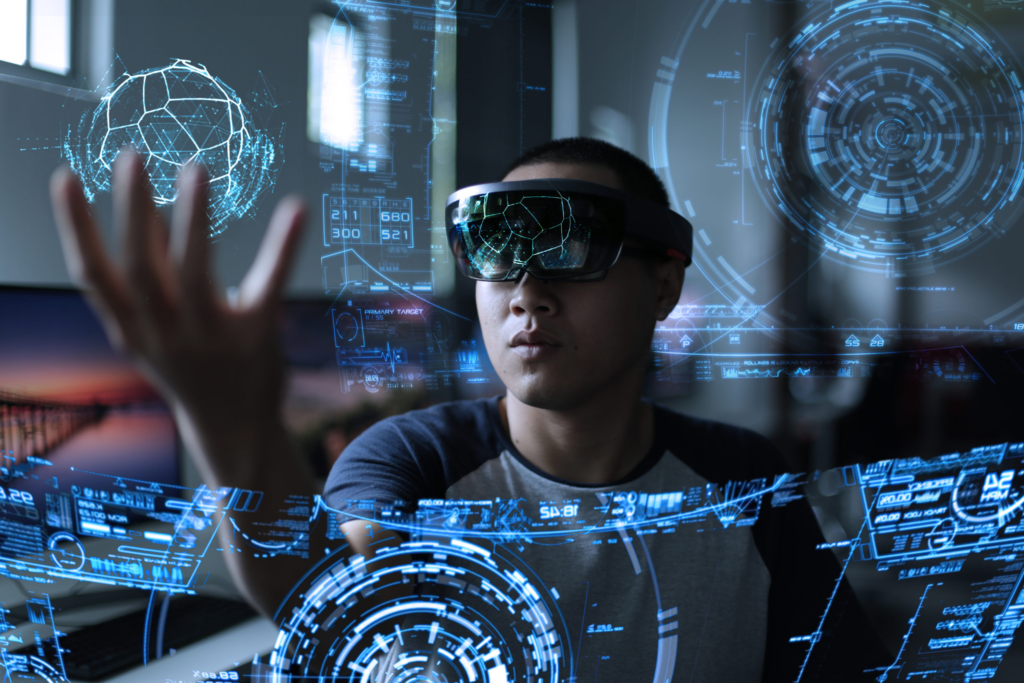

What’s next for AR in education apps? Let’s look ahead.
AR + AI: Smarter, Adaptive Learning
- Combining AI with AR to adapt content to student learning style, pace, errors in real time.
- AI-driven content generation (e.g. auto-generate AR scenes from curriculum).
- Virtual tutors or agents in AR guiding the learner.
WebAR & Browser-Based AR Education
- AR experiences delivered through web browsers, without app installs. This lowers friction. Wikipedia
- Easier distribution in K–12, where app installs may be restricted.
Wearables & Next-Gen AR Devices
- AR glasses or headsets may become more affordable and widespread, shifting the user experience.
- Hands-free AR interaction could open new pedagogical possibilities.
Integration with VR, Mixed Reality & Metaverse
- Hybrid experiences where learners switch between VR immersion and AR in real contexts.
- Shared virtual-physical classrooms, spatial metaverse learning environments.
More Open Content Ecosystems & Authoring Tools
- Platforms for teachers to build AR lessons easily.
- Shared repositories of AR educational modules.
- Standardization (AR formats, APIs) to ease interoperability.
Research & Evidence-Based Deployment
- More randomized controlled trials and studies validating learning impact.
- Integration of persuasive system design to maintain sustained engagement. ResearchGate
Sample Outline & Content Ideas for Your AR Education App Pages
To help with your content planning or website, here’s a suggested structure and content ideas:
Homepage / Landing Page
- Hero banner: “Transform Learning with AR in Education Apps”
- Feature highlights: immersive visuals, content catalog, analytics
- Use-case snapshots
- Call to action (demo, download, pilot)
Features Page
- 3D model viewer, interactivity, collaborative AR
- Offline support, analytics, teacher dashboard
- Authoring tools, content import
Use Cases / Case Studies
- Example: Anatomy lab in AR
- Example: Virtual chemistry lab
- Example: Vocabulary AR
Blog / Resources Section
- “5 Benefits of AR in Education Apps”
- “How to Design an AR Science Module”
- Pilot stories: School X used AR apps, results
- Interviews with teachers
Pricing / Plans
- Free vs premium features
- School or district licensing
- Support, training, content services
About / Contact
- Team, mission, vision
- Partnerships with schools, research bodies
- Contact for pilot programs
Each page should incorporate your focus keyword and related terms in headings and body naturally.
Example SEO-Friendly Headers Using the Focus Keyword
Here are examples of how you can integrate the focus keyword “AR in education apps” in your headers:
- H1: AR in Education Apps – Transforming the Future of Learning
- H2: Benefits of AR in Education Apps for Students and Teachers
- H3: Use Cases Where AR in Education Apps Excels
- H4: Overcoming Challenges When Implementing AR in Education Apps
- H5: How to Measure Learning Impact of AR in Education Apps
Ensure the keyword doesn’t feel forced; maintain readability.
Tips to Keep the Tone Simple, Human, and Engaging
Since you asked for a simple and humanized style, here are tips integrated into this article:
- Use natural language: Speak to the reader (e.g. “you,” “learners,” “students”)
- Give relatable examples: e.g. “point your phone at a plant to see root systems”
- Use analogies: e.g. “AR acts like a “magic lens” over your textbook”
- Break down jargon: Explain technical terms right away
- Short paragraphs and bullet lists: Easier scanning and readability
- Include stories or pilot snapshots: e.g. “In Turkey, students used Arloopa to visualize lungs and found the lesson more fun.” ERIC
- Encourage action: Ask questions (“Wouldn’t it be great if your students could rotate a DNA model in front of them?”)
Conclusion & Call to Action
AR in education apps holds immense potential to reshape learning—making lessons more engaging, meaningful, and effective. While there are challenges in hardware, content creation, and adoption, the right design, pedagogical alignment, and iteration can overcome them.
If you’re building or planning an AR educational app:
Market through SEO, content, and case studies
Begin with your learning objectives
Design simple, intuitive AR interactions
Pilot in small settings and learn from feedback
FAQs About AR in Education Apps
Here are the most commonly asked questions about AR in education apps and their answers:
Q1. What is AR in education apps used for?
A: AR in education apps helps students visualize complex topics, conduct virtual experiments, and explore subjects interactively. It’s used in fields like science, medicine, engineering, and even art.
Q2. How is AR different from VR in education?
A: AR overlays digital content onto the real world (through a phone or tablet), while Virtual Reality (VR) immerses users in a completely virtual environment using headsets.
Q3. Do AR education apps need special devices?
A: Most AR apps work on regular smartphones and tablets with cameras. However, more advanced experiences might require AR glasses or high-performance devices.
Q4. Can teachers create their own AR lessons?
A: Yes! Tools like Unity, Vuforia, and WebAR platforms allow teachers to design simple AR lessons without coding knowledge.
Q5. Are AR education apps expensive to develop?
A: Costs vary depending on features and 3D content quality. Basic AR apps can start at a few thousand dollars, while complex ones with AI integration can cost more.
Q6. What age group benefits most from AR in education apps?
A: AR works for all ages — from playful AR storybooks for toddlers to advanced anatomy or engineering tools for college students.
Q7. Do AR apps work offline?
A: Some AR apps offer offline features, but many require internet access to load 3D assets or cloud-based lessons.
Q8. What are the disadvantages of AR in education apps?
A: Common drawbacks include high development cost, hardware dependency, and potential distractions if not integrated properly.
Q9. Is AR in education just a trend?
A: Not at all. AR is evolving rapidly and is being adopted globally in schools and universities. It’s becoming a core part of digital education.
Q10. What is the future of AR in education apps?
A: The future involves smarter AI-driven AR systems, WebAR access without downloads, AR glasses, and immersive virtual classrooms.
Final Thoughts
The rise of AR in education apps represents one of the most exciting shifts in modern learning. It bridges imagination and understanding, transforming classrooms into creative spaces where curiosity thrives.
As technology grows, AR will become as common as textbooks — making education more accessible, interactive, and impactful.



I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://accounts.binance.com/sl/register?ref=I3OM7SCZ
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.